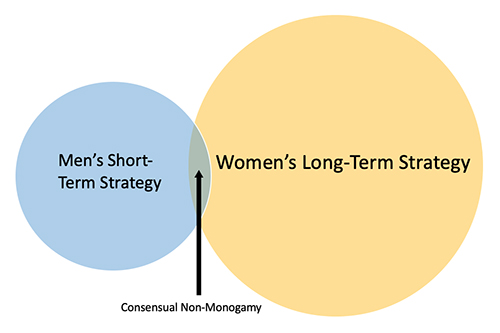
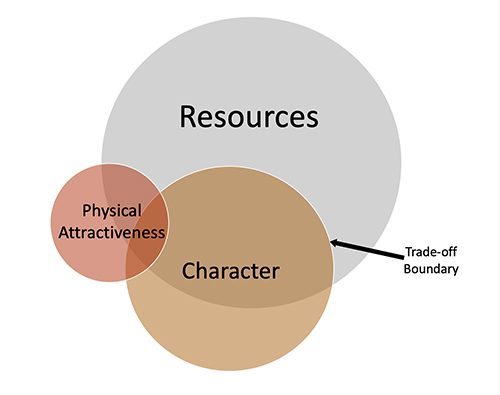
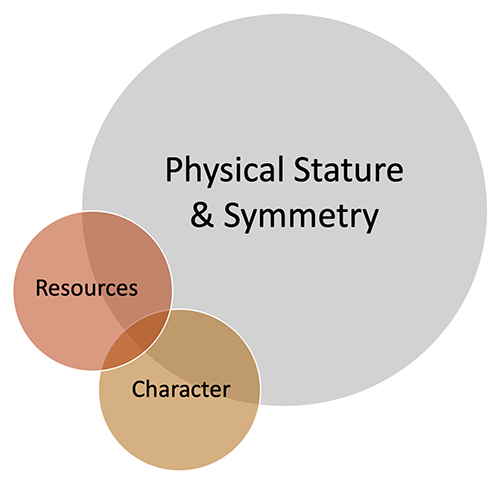
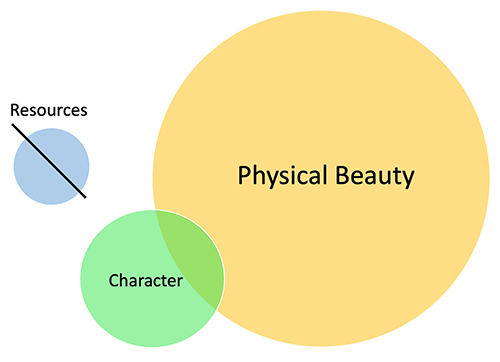
Evolutionary Science and Our Political Divide: The Root of It – Part 1
Male competition for mates and sex differences are first cause in human political affairs.
Since the advent of agriculture in human societies, nearly all impulses for male power and authoritarianism, and expressions of male dominance in a social hierarchy, have ultimately been the result of men competing for sexual access to women. All disputes over territory and wars between nations have their roots in out-group competition and the rewards of that competition for increasing mating opportunities. All causes of the unequal distribution of resources throughout all of human history are linked causally to the male reproductive strategy.
All impulses to check male authoritarianism come from men and women who lack resources and equality and exist at the lower end of a social hierarchy. Women primarily lead the charge to check the impulses of authoritarian men unless they want to mate with them. Liberal policies that strive to equitably distribute resources are more frequently backed by women.
Conservatives, and especially conservative men with power, are mostly interested in pursuing and maintaining male dominance and resist policies and governmental rules that change the status quo. Conservatives are most aligned with male needs and a male mating strategy. Liberals policies are more linked to a female mating strategy which focuses on the caretaking of children and other human beings.
Evolutionary Politics
The application of evolutionary science to our current political environment is quite revealing and instructive. In Sex, Power, and Partisanship: How Evolutionary Science Makes Sense of Our Political Divide (2019), Hector Garcia explores how evolutionary adaptations explain and predict our Left-Right political divide and a litany of issues. This post (and the one to follow) relies heavily on Garcia’s insights and the book’s 533 references of scholarship covering a broad range of disciplines.
Garcia applies the evolutionary lens to conservatism versus liberalism, equality versus hierarchy, and “big ape” authoritarianism; he reveals the “politics” of human mating strategies as a story of resource acquisition, sexual control, and the power of tribes. The underbelly of our political instincts has deep ancestral roots.
Planting and Staying Put Changed Everything
The study of human evolution shows that for most of our existence as a species, individual and community interests were in rough equilibrium. Our forging ancestors sought status, like all primates, but they generally acquired the highest status by doing things that benefited the group. Hunter-gatherers kept greed in check by employing guilt and shame among the group. Cooperation was essential to survival. Before agriculture, there were restraints on competition and evidence of coordination inside of the tribe.
With the advent of agriculture and civilization, a split began to occur. Individuals could acquire hitherto unimaginable status by accumulating wealth and power – often at the expense of family and community. Once agriculture drove out foraging, the need to cooperate was no longer essential to survival. It became every man for himself, except competition between tribes (out-groups) led to the development of coalitions and subsequent war between tribes and nations.
Size of the Tribe and Food Storage
Hunter-gatherer “tribes” tended to range in size from an extended family to a larger band of no more than about 100 people. Tribe-size groups were easier to regulate from within because hunter-gatherers could not store vast amounts of food to leverage their power base; there were limits to how much wealth and influence they could acquire. But when humans began to master agriculture, things changed drastically. Men used this power to achieve reproductive success in a zero-sum game. Zero-sum games are the root of inequality.
The Split
In the United States, the split between individual interests and community interests has become embedded in two ideologies: conservativism and liberalism. Conservatives promote individual freedom and self-reliance, primarily defined as freedom from government. Liberals promote fairness and equality and freedom from injustices suffered by a large segment of the community. In a later post, I will explain the foundations of morality that have shaped these positions. It is actually more complex than “individual vs. community,” but self-interest and the common good exist in a state of tension in most political ideologies. Understanding the moral foundations of conservatives and liberals is the only way for us to “listen to learn” from one another.
“Daddy Party” and “Mommy Party”
Republicans protect us with strong national defense; Democrats nourish us with Social Security and Medicare. Republicans worry about our business affairs. Democrats look after our health, nutrition, and welfare. It’s the traditional American family. “Daddy” locks the door at night and brings home the bacon. “Mommy” worries when the kids are sick and makes sure each one gets treated fairly. ~ Chris Mathews (1991).
Gender/Sex and Political Affiliations
The existence of a fundamental gender gap in American political party affiliation has been reported for years. In 2009, Gallop concluded their survey analysis with this: “The fact that the gender gap persists not only across age groups, but within major racial, ethnic, and marital-status groups, reinforces the conclusion that a gender difference in political orientation is a fundamental part of today’s American political and social scene.”
In 2020, the gender gap has widened even more. The New York Times/Sienna College poll of July 16, 2020, found that women favored Biden by 22 points. White women with a college degree favored Biden by 39 points. The Wall Street Journal poll in August of 2019 found that white/non-college men favored Trump by 45 points, 67-22 percent.
“Barring a giant polling error, the 2020 election will witness the largest gender gap in partisan preference since women gained the franchise” (New York Intelligencer, “Men and Women Have Never Been More Politically Divided,” October 19, 2020).
Stereotypes and Political Affiliation
Political scientist Nicolas Winter looked at US survey data from the American National Election Study from 1972 to 2004 and that found voters overwhelming used more masculine stereotypes to describe GOP candidates and more feminine characteristics to describe Democrats.
In another study (2006), political scientist Monika McDermott administered the Bem Sex Role Inventory (BSRI) to 780 Americans, along with a series of questions about their political beliefs and behavior. The BSRI is one of the most widely used instruments to assess gendered psychology. For feminine traits, the BSRI asks participants to rate how much the following descriptors apply to him or her: “understanding, sympathetic, warm, loves children, compassionate, gentle, eager to soothe hurt feelings, affectionate, sensitive to the needs of others, and tender.” Masculine traits were described as “willingness to take risks, forceful, strong personality, assertive, independent, leadership ability, aggressive, dominant, willing to take a stand, and defends own beliefs.”
McDermott found that men and women who scored high on femininity were significantly more likely to identify as Democrat, and men and women who scored high on masculinity were more likely to identify as Republican.
Why Do Sex-Based Partisan Differences Exist?
Political partisanship arises from sex-based approaches to perpetuating our genes. Conservatism is a male-centric strategy shaped by the struggle for dominance in male competitions within-and-between groups, while liberalism is a female-centric strategy derived from the protracted demands of rearing human offspring.
Not all men enact a conservative strategy, nor do all women enact a liberal strategy. But we do see sex-based leanings — two bell curves, one tilting toward the political right for men, and one tilting to the left for women, with significant overlap between the curves.
Partisan Politics and Reproductive Dominance
The tribalistic flavor (us vs. them) of political conservatism, with its emphasis on female sexual control and hawkish territorial nature, is rooted in male mate competition – the ageless biological struggle for reproductive dominance. Male competition for women turns out to be the core driving force behind political issues.
The winner-take-all mentality of conservative economic policy is based on male competition for mates. War is team-based male-mate competition. The coalitionary psychology of men was forged by the risk of being annihilated by the outside tribe – and the potential gains of taking over the rival tribes’ territory, resources, and women. Militaristic logic embedded in that psychology maps squarely onto the hallmark values of political conservatism. It is from the context of violent male mate competition and its most heightened expression, war, that we are able to most fully understand the masculine tenor of conservative political psychology.
Roots of Liberalism
The roots of liberalism have arisen from the timeless effort to rein in dominant males and to prevent them from monopolizing resources and impinging on the evolutionary fitness of those with less power. Liberalism is based on the prodigious human task of raising children, a critical survival enterprise championed by women and provisioned by the “Mommy” parties of the world.
Big Five Personality Traits
Social scientists have developed various models for understanding human personality, the most widely researched of which is known as the “Big Five.” The Big Five personality traits are openness to experience, conscientiousness, extroversion, agreeableness, and neuroticism. Cross-cultural studies strongly suggest that Big Five patterns of interacting with the world are genetically based universals. Human personality traits, especially openness to experience, reliably correlated to political orientation.
Liberal Openness
Openness to experience is a hallmark of the liberal political orientation. This personality dimension reflects not only an openness to new things, policies, and programs, but also to other people. Liberals demonstrate xenophilia, an attraction to new cultures, and even outsiders. High openness is also related to sensation-seeking and a general appreciation for novelty and adventure. There is a moderate correlation of openness to the trait of extroversion – the tendency to be talkative and seek social interaction.
One large study (Gerber et al., 2010) of over twelve thousand Americans examined the Big Five personality traits as predictors of core social and economic values, as well as self-reported political ideology (a five-point scale ranging from very liberal to very conservative). The authors found that higher openness was associated with greater liberalism across all three measures of orientation.
Conservatives Fear Disease and Outsiders
Could fear of disease translate into fear of outsiders and political conservatism? Research has shown that individuals who have a higher perceived threat of disease show more ethnocentrism, greater xenophobic attitudes toward foreigners, and increased willingness to stigmatize socially marginalized groups. This is particularly ironic in the time off Covid-19 but will make sense in the context of conservative “moral foundations” described in a future post in this series.
Xenophobia: Membership Has its Privileges
Xenophobia is a dislike of outsiders and a corresponding preference for in-group members and values. This is not just about “outside” people and their physical differences, but also about differences related to language, customs, dress, sexual orientation, religion, nationality, political party, and even sports teams. This preference often manifests as a sense of patriotism and loyalty. Conservative political ideology predicts prejudice against an outside group. If xenophobia reflects an adaptation that helped our ancestors avoid contagious diseases from outsiders, we would expect to see xenophobia in modern times and conservatives exhibiting more fear of contagion.
Patrilocality and Human Warfare
Historically, humans have been mostly patrilocal – that is, women often left their natal group (i.e. more adapted to outsiders) whereas men stayed put with their male relatives. The resulting concentration of male blood relatives encouraged strong, trusting, and cooperative male bonds based on shared genes. The love and trust that related men have for one another have had profound implications for the human condition across time. Higher relatedness gave men greater confidence in risky cooperative enterprises, such as war. Patrilocality in human groups is associated with more frequent warfare.
Human Males Are Like Chimpanzees
Primatologists Richard Wrangham and Dale Peterson write that among four thousand mammals, only chimpanzees and humans follow this pattern of patrilocality, accompanied by “a system of intense, male-initiated territorial aggression, including lethal raiding into neighboring communities in search of vulnerable enemies to attack and kill.” Chimpanzee males are extremely hostile to outside males, thus males rarely transfer between groups. Any male attempting to transfer would be killed by the males of the out-group. By contrast, 50-90 percent of female chimpanzees transfer to other groups to breed once they reach sexual maturity. Whereas male transfers are seen as sexual competitors carrying foreign genes, females are welcomed as potential mating partners. (Again, the female-centric roots of xenophilia.)
Xenophobia and Band of Brothers
Thus, xenophobia is concentrated among men and has caused real dangers for them. Most of the world’s perpetrators of violence are men, but most of its victims are also men. The United Nations recently found that globally, 80 percent of homicide victims are men.
If ancestral men could not leave their group for fear of death, then turning inward to their band of brothers, remaining xenophobic toward outsiders, and favoring dominance over other groups was evolutionarily sensible. The over-representation of men among conservatives and the preponderance of male interests embedded in conservative ideologies reflect these ancient selection pressures on men. (I will come back to xenophobia in post #2 of this series.)
Conservatives Are “Disgusted”
Research consistently finds a higher disgust sensitivity related to self-placement on the Left-Right spectrum. One study of 31,045 men and women from 121 countries found that those who self-rated as conservative showed significantly higher disgust sensitivity than those who self-rated as liberal.
Disgust sensitivity (as well as fear of disease) can translate into fear of outsiders. Researchers found that those with higher disgust sensitivity were more likely to see immigrants and foreign ethnic groups as less than human, and scored higher on measures of political conservatism, social dominance orientation, and right-wing authoritarianism. Research in this area links the fear of pathogens to disapproval of nonnormative sexual behaviors, which suggests that our sexual morality is rooted in adaptations designed to help us survive reproduction in a world filled with pathogens. (I will address social dominance orientation and right-wing authoritarianism more in-depth in the next post.)
Conservatism, Conscientiousness, and Closed Systems
Conscientiousness (a Big Five personality trait) is consistently associated with political conservatism. Conscientiousness relates to orderliness and control of one’s environment. According to a study by Alain Van Heil and colleagues reported in the Journal of Personality, a preference for closed systems is related to cognitive rigidity, or lower cognitive complexity – the ability to grasp alternative perspectives or dimensions and synthesize those varying perspectives into a cohesive framework. An example offered by Garcia: saying “All immigrants are criminals,” instead of reasoning, “Some immigrants my commit crimes, but many do not, and there are a variety of factors that may lead to such behaviors” (p. 60).
Conservatives Are More Rule-oriented
Related to conscientiousness, conservatives in the US score higher than liberals on measures of following rules. This is linked to the conservative value of traditionalism and dedication to the existing way of doing things – a resistance to social change. Conservatives tend to favor harsher punishment for rule-breakers, such as the death penalty and longer prison sentences.
Political Affiliation and the Autistic “Male” Brain
One theory that might explain the conservative, male-centric personality is proffered by British developmental psychologist Simon Baron-Cohen. He argues that autism is an extreme variant of the male brain. Autism is over-represented by males in a 10-1 ratio. Baron-Cohen also describes how men prefer “closed systems” that are predictable, factual, rule-based, knowable, and to some extent, controllable. Again, these ways of processing information are linked more reliably with the “conscientiousness” of conservatism and in opposition to the “openness to experience” of political liberals.
Theory of Mind
Important differences between females and males that Baron-Cohen uses to explain autism are glaringly present between liberals and conservatives. Being able to read the mind of another human (thoughts, emotions, intentions) is called theory of mind (ToM). The inability to read minds is one of the hallmarks of autism. There is much evidence that women outperform men on theory of mind (ToM) tasks and are better at understanding the minds of others.
Brain Morphology and Theory of Mind
The brains of men and women (morphology and function) exhibit vastly more similarities than differences. Even so, existing differences have meaningful implications for our political psychology.
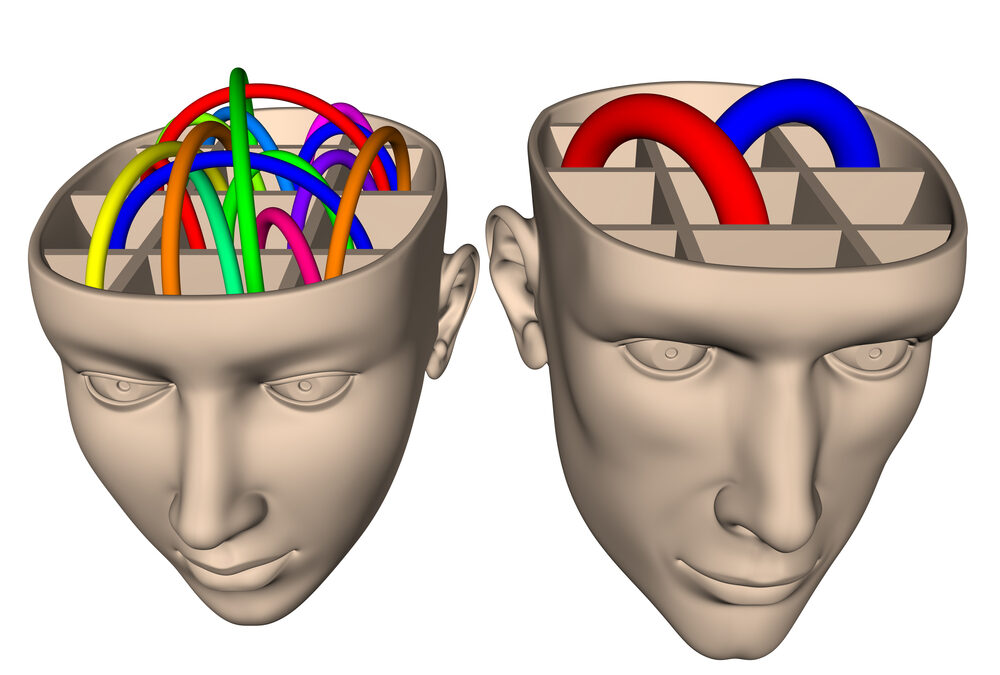
While few studies to date have measured the difference in the theory of mind between liberal and conservatives, two neuroimaging studies give us some interesting clues. One study measured gray-matter volume and found those self-identified as liberal exhibited greater volume in the anterior cingulate cortex, a brain region implicated in the theory of mind and feeling the pain of others. Conservatives had greater brain volume in the amygdala — the fear center of the brain.
Another study examined MRIs of Republicans and Democrats. Republicans showed greater activation in the amygdala, and Democrats had more activation in the cingulate insula, a brain region also activated in theory of mind tasks. Mindreading differences between liberals and conservatives may be a function of differences in brain structure.
Women and Liberals Show More Empathy
Any research finding of difference between women and men will have a rough correlation to differences between liberals and conservatives, respectively. For instance, women score higher on questionnaires that measure empathy. Girls from one year of age show more empathy to others’ suffering than do boys. Liberals show more signs of distress about violence and suffering than conservatives and tend to score higher on empathy measures.
Language, Gender, and Political Affiliation
Women have better language skills. A Gallup poll (2001) found that those who identified as being liberal were more likely to be bilingual than moderates or conservatives. Other studies show that liberals score higher than conservatives on verbal ability and vocabulary tests. (And girls develop vocabularies faster than boys.) Lower verbal ability has also been associated with right-wing authoritarianism and a high social dominance orientation. (I would gladly supply the eight studies behind this section upon request.)
Fairness and Turn-taking
Females are generally more concerned with fairness and males are more concerned with dominance hierarchies. These tendencies are observed early. One study found that girls exhibited twenty times more turn-taking than boys and boys exhibited competitive behaviors fifty times more than girls. Boys often form dominance hierarchies. Girls, on the other hand, spend more energy trying to solve differences using politeness, tact, and diplomacy. Boys are more incline to intra-group and intergroup dominance. Boys don’t let losers forget who won. Girls more often try to make the players feel equal and deemphasize who won. Intergroup dominance among male competitors continues into adulthood and is seen everywhere from professional sports teams to street gangs to militaries.
Primacy of Fairness for Liberals
In my next post, I will expound at length about the moral foundations of liberalism and conservativism. Suffice to say now, the concept of fairness (meaning equality) is a sacred value for liberals. In one large international study (34,476 subjects) conducted by Jesse Graham, liberals agreed to such statements as “when the government makes laws, the number one principle should be ensuring that everyone is treated fairly.” Graham found that fairness concerns are reliably higher among those identifying as liberals.
Conservatives and Social Hierarchy
Conservatives are more comfortable with social hierarchies, tend to oppose policies such as affirmative action, and participate little in efforts to redirect social wealth. Research has found that conservatives score higher on the Social Dominance Orientation scale (SDO). In my next post, I will explore and assert the benefits of a conservative framework that are somewhat independent of their comfort with social hierarchies.
“Conservatives” Helped Our Ancestors Survive – a Prologue to Moral Foundations
There is a significant relationship between conservatism, masculinity, physical stature, spatial abilities, and many other adaptations that are geared for using violence to survive a harsh, ancestral environment. There is evidence that less empathy among men has fitness benefits. A lack of empathy has utility in male mate competition and for killing in warfare. Natural selection doesn’t care what traits get passed on. Sometimes the advantage can involve empathy, and at other times, suppressing it. It is not difficult to imagine how suppressing empathy would help in the heat of battle. In a similar vein, intolerance for ambiguity would be useful in dangerous environments such as combat. When the stakes are life and death, it makes more sense to think in black and white terms.
Conclusion of Post #1 — The Roots of Our Political Divide
The differences found between men and women related to cognition, affect, language, social behavior, and brain morphology, strongly mirror the same differences between liberals and conservatives and are directly correlated to male and female mating strategies. “Stereotypes about liberalism having a feminine quality and conservatism a masculine one, have empirical backing and are rooted in our neuropsychology, which was shaped by selective pressures of the natural and social environments of our ancestors. In turn, our evolved political orientations reflect those pressures. While there have been many explanations for what drives our political stances, few have as much explanatory power as the strategies we employ to survive and reproduce” (Sex, Power and Partisanship. p.64-65).
Stayed tuned for Post #2 in this Series, the Roots of Our Political Divide
In the next post (#2 of “Roots”), I will address social dominance orientation (SDO), right-wing authoritarianism, the politics of sexual control, and much more. After that, I will unveil the brilliant work of Jonathan Haidt on the moral foundations of liberalism, conservativism, and libertarianism, and address related issues of motivated reasoning in the post-objectivity era.
References
Gerber, A. et al., (2010). “Personality and Political Attitudes: Relationships across Issue Domains and Political Contexts,” American Political Science Review, 104.
Graham, J. et al., (2011). “Mapping the Moral Domain,” Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 101.
Kanai, R. et al., (2016). “Political Orientations Are Correlated with Brain Structure in Young Adults,” Current Biology 21, no. 8.
McCue, C. & Gopoian, D., (2000). “Dispositional Empathy and the Political Gender Gap,” Women & Politics, 21, No. 2.
McDermott, M., (2016). Masculinity, Femininity, and American Political Behavior.
Schreiber, D. et al. (2013). “Red Brain, Blue Brain: Evaluative Processes Differ in Democrats and Republicans,” PLoS ONE 8, no. 2.
Van Heil et al., (2010). “The Relationship between Social-Cultural Attitudes and Behavioral Measures of Cognitive Style: A Meta-Analytic Integration of Studie,” Journal of Personality 78, no. 6.
Please Note: Your comment may take up to 12 seconds to register and the confirmation message will appear above the “Submit a Comment” text.